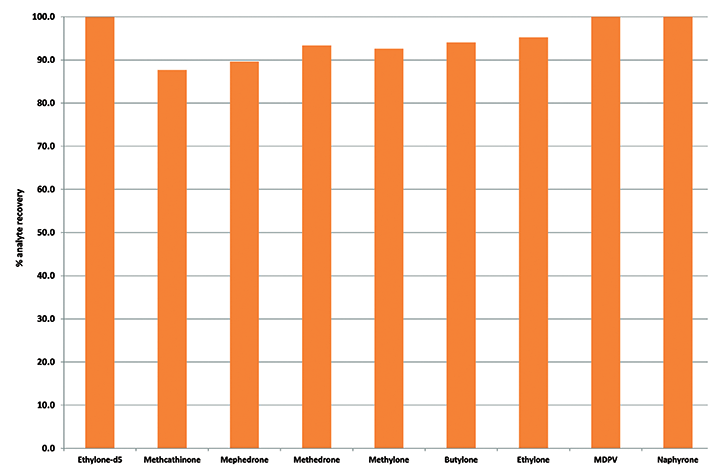
This sample preparation method to extract and analyze ‘Bath Salts’ uses ISOLUTE SLE+, a Supported Liquid Extraction product, that offers an efficient alternative to traditional liquid -liquid extraction (LLE) for bioanalytical sample preparation, providing high analyte recoveries, no emulsion formation, and significantly reduced sample preparation time. Analyte recoveries achieved using this method ranged from 87-99% with RSDs below 10% for all analytes and linearity in the range of 5-250 ng/mL.
Introduction ‘Bath salts’ is the street name for a family of designer drugs chemically similar to cathinones that give the user similar effects to amphetamines. The abuse of these drugs is on the increase and regulation against their use and supply has now been implemented in the EU and North America.
Method
Column configuration:
ISOLUTE SLE+ 1 mL Sample Volume column, part number 820-0140-C
Sample pre-treatment:
Dilute urine 1:1 (v/v) with 150 mM ammonium hydroxide.
Sample loading:
Load the pre-treated sample (1 mL total volume) onto the column and apply a pulse of vacuum (VacMaster 20 Sample Processing Manifold, 121-2016) or positive pressure (PRESSURE+ 48 Positive Pressure Manifold, PPM-48) to initiate flow. Allow the sample to adsorb for 5 minutes.
Analyte extraction:
Apply MTBE (2 mL) and allow to flow under gravity for 5 minutes. Apply a further aliquot of MTBE (2 mL) and allow to flow under gravity for another 5 minutes. Apply vacuum or positive pressure to pull through any remaining extraction solvent, collecting into a glass culture tube containing 0.2 M hydrochloric acid (100 µL) to add stability during evaporation.
Post extraction:
Evaporate the extract to dryness (ambient temperature). Add pentafluoropropionic acid anhydride (PFPA) (50 µL) and ethyl acetate (50 µL) for derivatization. Vortex for 20 seconds, transfer to a high recovery glass vial and cap with a non-split cap. Heat vial in a heating block (70 ºC) for 20 minutes. Remove vial and allow to cool. Evaporate the mixture to dryness (ambient temperature). Reconstitute in dichloromethane:isopropanol (95:5, v/v) (100 µL). Cap with a non-split cap and vortex for 30 seconds.
Results
Extracted samples were quantified using an Agilent GCMS (7890A/5975)with an SGE capillary column (30mx0.25mmx0.25µm). Analyte recoveries achieved were 87-99% (n=7) with RSDs below 10% for all analytes and linearity in the range of 5-250 ng/mL with an r2 coefficient of 0.99.
Conclusion
This method shows that ISOLUTE SLE+ is well suited in efficient clean up and extraction of these new substituted cathinone drugs from urine, giving high analyte recoveries and low quantitation limits.
Download the Full Application Note here.






